PART 12: EIGRP STUB
Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol
EIGRP stub routers play a critical role in optimizing network convergence and resource utilization in hierarchical network designs. This feature helps limit query propagation and reduce unnecessary control plane traffic in specific network topologies.
Purpose and Benefits of EIGRP Stub Routers
EIGRP stub configuration is designed primarily to:
Limit EIGRP query scope during route failures
Reduce bandwidth consumption on WAN links
Accelerate network convergence
Minimize processing requirements on edge devices
Protect remote routers from participating in complex route calculations
Common Deployment Scenarios
Remote Office/Branch Office
In a typical enterprise network, small remote offices connect to headquarters via limited-bandwidth WAN links. Without stub configuration, these remote routers would:
Receive all query messages for any route failure in the core network
Consume valuable WAN bandwidth with query/reply traffic
Process queries for routes they have no alternate path to reach
Hub-and-Spoke Topologies
In hub-and-spoke designs, spoke routers only have a single path back to the network core. Configuring these as stubs prevents unnecessary query propagation while maintaining full connectivity.
EIGRP Stub Operation
When a router is configured as a stub:
It sends special Hello packets containing a Stub TLV (Type-Length-Value) field
This TLV identifies the router as a stub and indicates its capabilities
Upstream neighbors will not send queries to the stub router for route information
The stub router will only advertise routes according to its configured stub options
The upstream neighbor effectively acts as a shield, answering queries on behalf of the stub router by immediately replying "unreachable" for routes not in its own table.
Stub Configuration Options
TLV Flag Behavior
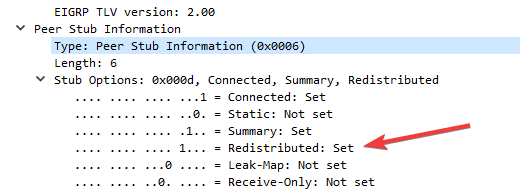
As shown in the image, the stub capabilities are encoded in a bit field within the Stub TLV:
Connected: Set (1)
Static: Not set (0)
Summary: Set (1)
Redistributed: Set (1)
Leak-Map: Not set (0)
Receive-Only: Not set (0)
Notably, the "redistributed" bit is set by default in the TLV, even if not explicitly configured, though it will only take effect for connected routes unless explicit redistribution is configured.
Configuration Commands
Cisco IOS/IOS XE (Numbered Mode)
Router(config-router)# eigrp stub [connected] [static] [summary] [redistributed] [leak-map name] [receive-only]Cisco IOS XE (Named Mode)
Router(config-router-af)# eigrp stub [connected] [static] [summary] [redistributed] [leak-map name] [receive-only]Important Considerations
Static routes require either network statements or redistribution to be advertised
Default advertisement includes connected and summary routes only
Neighbor reestablishment occurs when stub configuration changes
Redistributed bit appears set in packet captures by default, but only applies to connected routes unless redistribution is configured
Receive-only option cannot be combined with any other stub options